Tuberculosis Risk Assessment
At the Whitley County Health Department, your well-being is our top priority. That’s why we offer comprehensive Tuberculosis (TB) risk assessment and direct observation therapy to support your health journey. Direct observation therapy involves one of our healthcare professionals observing you while you take your TB medication. This not only ensures that you’re taking the right doses but also helps us address any questions or concerns you may have about your treatment. Our goal is to make the process as seamless as possible, helping you focus on your health.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. While it typically affects the lungs, it can also target other parts of the body like the kidney, spine, and brain. It’s important to note that not everyone with TB bacteria gets sick. There are two TB-related conditions: latent TB infection (LTBI) and TB disease. If TB disease is not treated properly, it can become serious, so early detection and treatment are crucial for your health.
Learn More: What You Need to Know About Tuberculosis
Signs & Symptoms
The symptoms of TB disease vary depending on the part of the body where TB bacteria are growing. Typically, TB bacteria thrive in the lungs, leading to pulmonary TB.
Symptoms of TB disease in the lungs may include:
- A persistent cough lasting three weeks or more
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs)
Additional symptoms of TB disease encompass:
- Weakness or fatigue
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Chills
- Fever
- Night sweats
Symptoms of TB disease in other parts of the body are contingent on the affected area.
Individuals with latent TB infection:
- Do not feel sick
- Do not exhibit any symptoms
- Cannot transmit TB to others
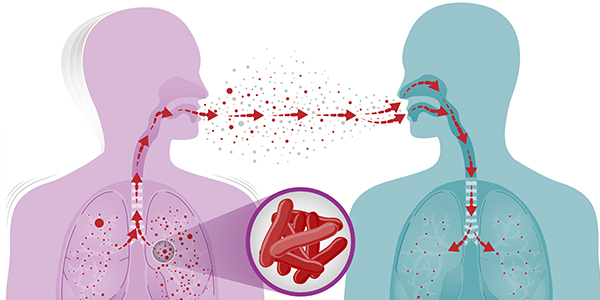
How TB Spreads
Tuberculosis (TB) bacteria are transmitted through the air when a person with TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs, speaks, or sings. In these instances, TB bacteria become airborne, and individuals nearby may inhale these bacteria and become infected.
It’s important to note that TB is NOT spread through:
- Shaking someone’s hand
- Sharing food or drink
- Touching bed linens or toilet seats
- Sharing toothbrushes
- Kissing
When TB bacteria are inhaled, they settle in the lungs and start to grow. From there, they can travel through the blood to other parts of the body, such as the kidney, spine, and brain. TB disease in the lungs or throat can be infectious, meaning it can spread to others. TB in other parts of the body, like the kidney or spine, is typically not infectious.
Individuals with TB disease are most likely to transmit it to people they interact with regularly, such as family members, friends, coworkers, or schoolmates.

